Protein is an essential macronutrient that helps build and repair muscles, organs, and tissues. It also supports the immune system, hormone production, and enzyme function. However, not all sources of protein are equal in terms of their health benefits and environmental impacts. In this article, we will compare vegan protein and animal protein, and show why vegan protein is healthier than animal protein.

What is vegan protein?
Vegan protein is any protein that comes from plant-based sources, such as beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, nuts, seeds, grains, and vegetables. Vegan protein can also be found in processed foods, such as vegan meat alternatives, vegan cheese, and vegan protein powders. Vegan protein is usually lower in calories, fat, and cholesterol than animal protein, and higher in fiber, antioxidants, and phytochemicals.
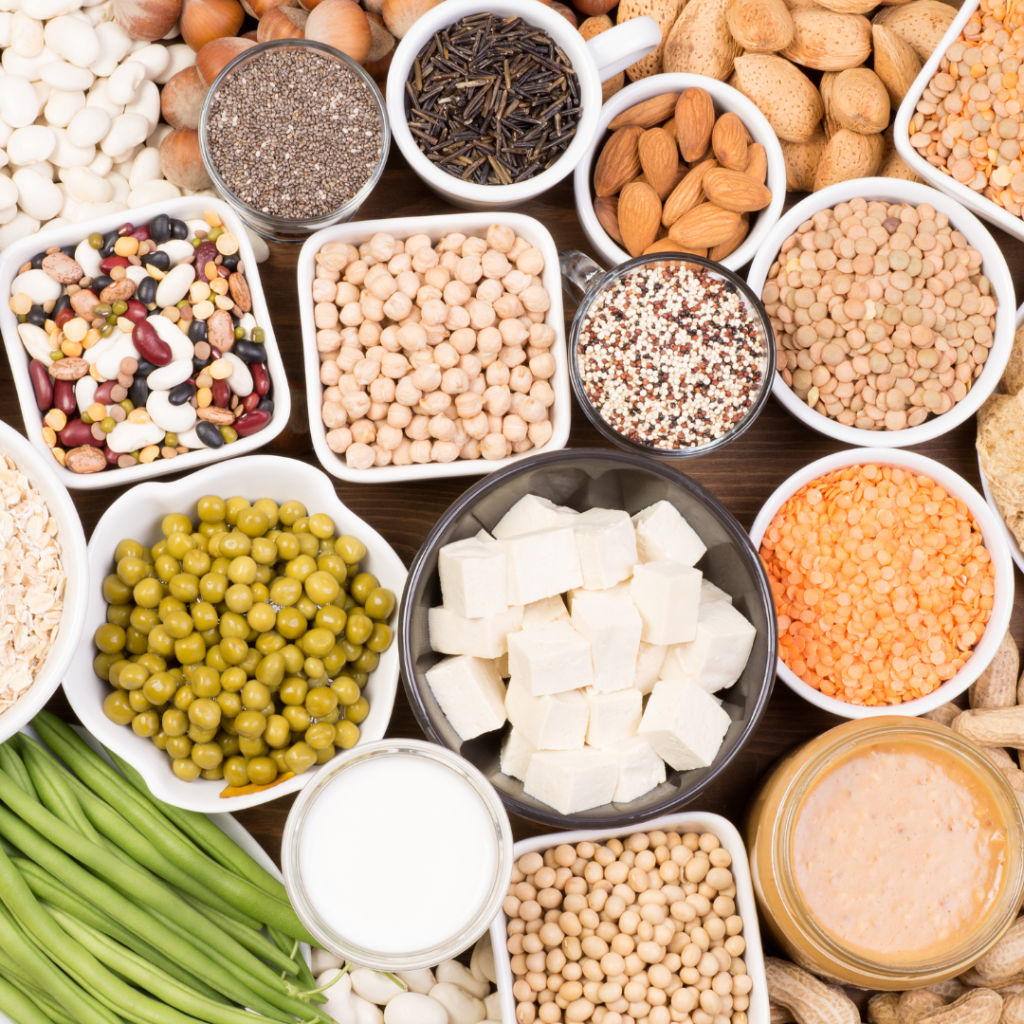

What is animal protein?
Animal protein is any protein that comes from animal sources, such as meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy, and honey. Animal protein is usually higher in calories, fat, and cholesterol than vegan protein, and lower in fiber, antioxidants, and phytochemicals. Animal protein can also contain hormones, antibiotics, and contaminants, such as pesticides, heavy metals, and dioxins.
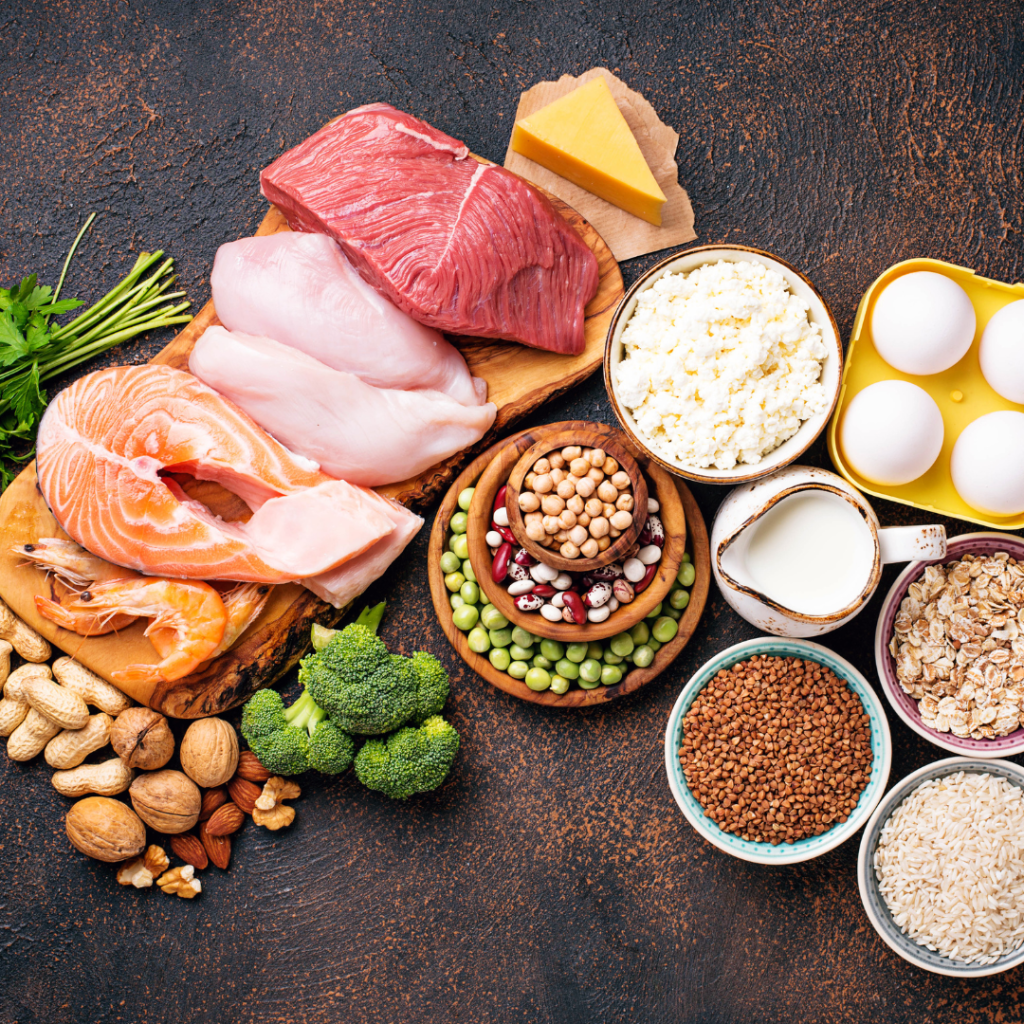

Why is vegan protein healthier than animal protein?
There are several reasons why vegan protein is healthier than animal protein, both for humans and the planet. Here are some of the main benefits of vegan protein:
- Vegan protein can lower the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, obesity, and some cancers. This is because vegan protein is lower in saturated fat, cholesterol, and sodium, and higher in fiber, antioxidants, and phytochemicals, which can help lower blood pressure, cholesterol, blood sugar, and inflammation. Vegan protein can also help prevent or reverse atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaque in the arteries that can lead to heart attacks and strokes.
- Vegan protein can improve digestion and gut health. This is because vegan protein is higher in fiber, which can help regulate bowel movements, prevent constipation, and feed the beneficial bacteria in the gut. Fiber can also help lower the risk of colon cancer, diverticulitis, and hemorrhoids. Vegan protein can also help prevent or treat irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, and other digestive disorders.
- Vegan protein can support healthy bones and muscles. This is because vegan protein is rich in calcium, magnesium, potassium, and vitamin K, which are essential for bone health and density. Vegan protein can also help prevent or treat osteoporosis, arthritis, and fractures. Vegan protein can also provide enough amino acids, the building blocks of protein, to support muscle growth and repair. Vegan protein can also help prevent or treat sarcopenia, which is the loss of muscle mass and strength due to aging.
- Vegan protein can benefit the environment and animal welfare. This is because vegan protein requires less land, water, and energy than animal protein, and produces less greenhouse gas emissions, waste, and pollution. Vegan protein can also help prevent deforestation, soil erosion, biodiversity loss, and water scarcity. Vegan protein can also help reduce animal suffering, exploitation, and slaughter.
Conclusion
Vegan protein is healthier than animal protein for many reasons. Vegan protein can lower the risk of chronic diseases, improve digestion and gut health, support healthy bones and muscles, and benefit the environment and animal welfare. Vegan protein can also provide all the essential amino acids and nutrients that the human body needs. Therefore, choosing vegan protein over animal protein can be a smart and compassionate decision for your health and the planet.
Por qué la proteína vegana es más saludable que la proteína animal
La proteína es un macronutriente esencial que ayuda a desarrollar y reparar músculos, órganos y tejidos. También apoya el sistema inmunológico, la producción de hormonas y la función enzimática. Sin embargo, no todas las fuentes de proteínas son iguales en términos de beneficios para la salud e impactos ambientales. En este artículo, compararemos la proteína vegana y la proteína animal y mostraremos por qué la proteína vegana es más saludable que la proteína animal.

¿Qué es la proteína vegana?
La proteína vegana es cualquier proteína que proviene de fuentes vegetales, como frijoles, lentejas, tofu, tempeh, nueces, semillas, cereales y verduras. La proteína vegana también se puede encontrar en alimentos procesados, como alternativas veganas a la carne, queso vegano y proteínas en polvo veganas. La proteína vegana suele tener menos calorías, grasas y colesterol que la proteína animal, y más fibra, antioxidantes y fitoquímicos.
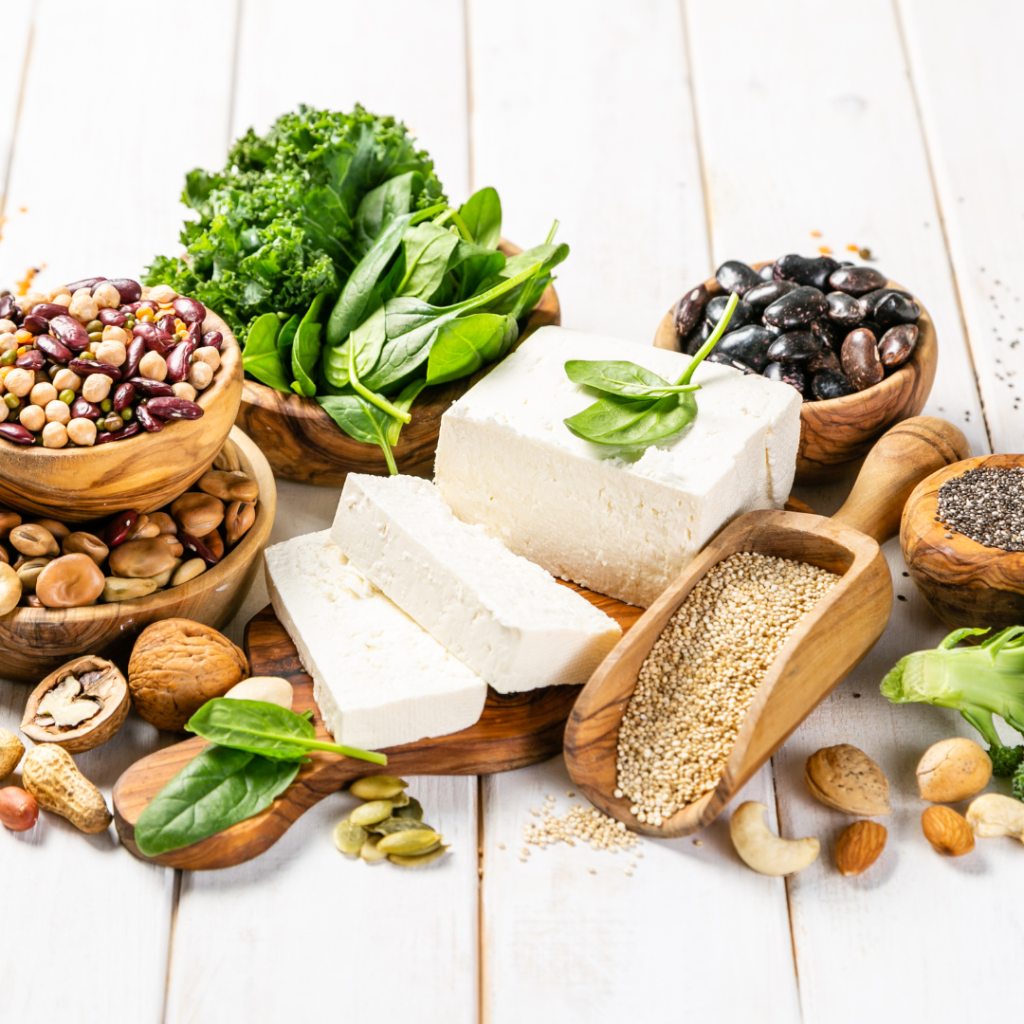

¿Qué es la proteína animal?
La proteína animal es cualquier proteína que proviene de fuentes animales, como carne, aves, pescado, huevos, lácteos y miel. La proteína animal suele tener más calorías, grasas y colesterol que la proteína vegana, y menos fibra, antioxidantes y fitoquímicos. La proteína animal también puede contener hormonas, antibióticos y contaminantes, como pesticidas, metales pesados y dioxinas.
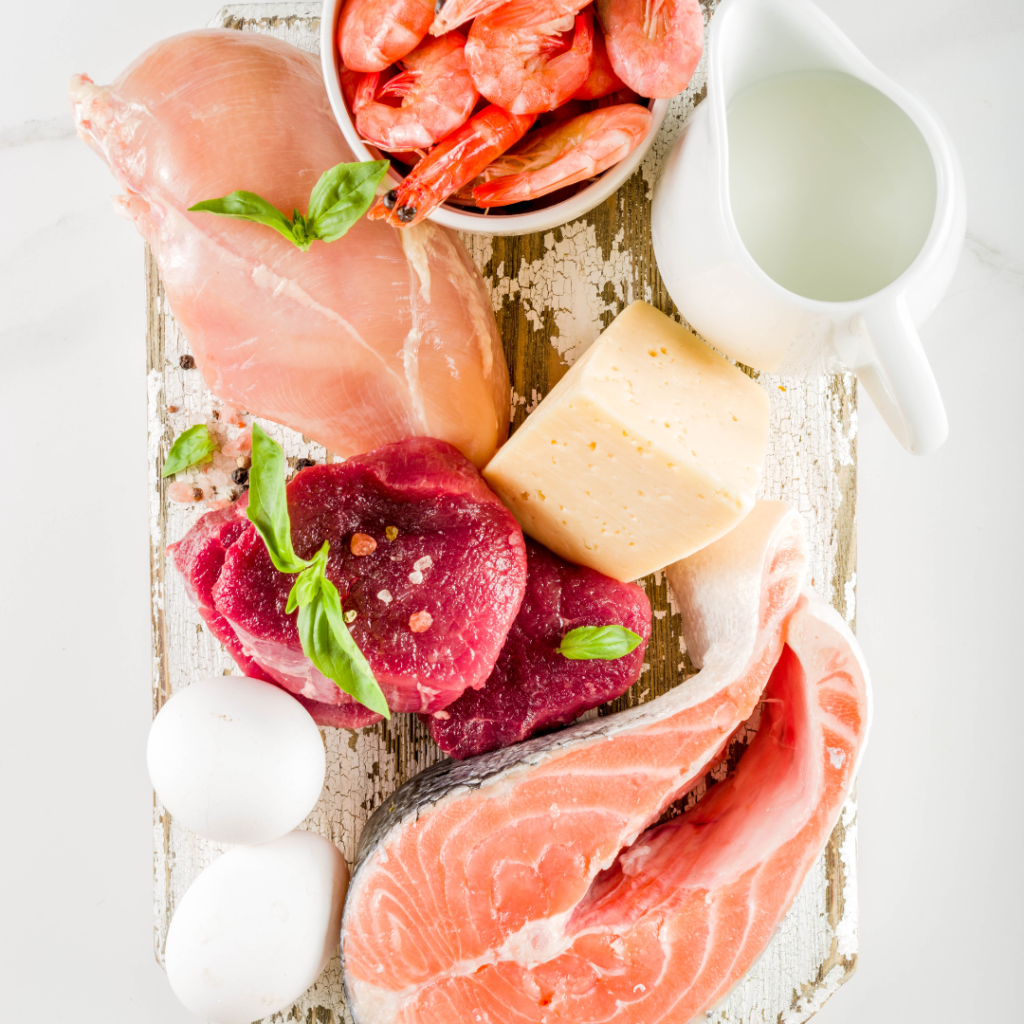

¿Por qué la proteína vegana es más saludable que la proteína animal?
Hay varias razones por las que la proteína vegana es más saludable que la proteína animal, tanto para los humanos como para el planeta. Estos son algunos de los principales beneficios de la proteína vegana:
- La proteína vegana puede reducir el riesgo de enfermedades crónicas, como enfermedades cardíacas, diabetes, obesidad y algunos cánceres. Esto se debe a que la proteína vegana tiene menos grasa saturada, colesterol y sodio, y más fibra, antioxidantes y fitoquímicos, que pueden ayudar a reducir la presión arterial, el colesterol, el azúcar en sangre y la inflamación. La proteína vegana también puede ayudar a prevenir o revertir la aterosclerosis, que es la acumulación de placa en las arterias que puede provocar ataques cardíacos y accidentes cerebrovasculares.
- La proteína vegana puede mejorar la digestión y la salud intestinal. Esto se debe a que la proteína vegana tiene un alto contenido de fibra, lo que puede ayudar a regular las deposiciones, prevenir el estreñimiento y alimentar las bacterias beneficiosas del intestino. La fibra también puede ayudar a reducir el riesgo de cáncer de colon, diverticulitis y hemorroides. La proteína vegana también puede ayudar a prevenir o tratar el síndrome del intestino irritable, la enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal y otros trastornos digestivos.
- La proteína vegana puede favorecer la salud de huesos y músculos. Esto se debe a que la proteína vegana es rica en calcio, magnesio, potasio y vitamina K, que son esenciales para la salud y la densidad ósea. La proteína vegana también puede ayudar a prevenir o tratar la osteoporosis, la artritis y las fracturas. La proteína vegana también puede proporcionar suficientes aminoácidos, los componentes básicos de las proteínas, para favorecer el crecimiento y la reparación muscular. La proteína vegana también puede ayudar a prevenir o tratar la sarcopenia, que es la pérdida de masa y fuerza muscular debido al envejecimiento.
- La proteína vegana puede beneficiar al medio ambiente y al bienestar animal. Esto se debe a que la proteína vegana requiere menos tierra, agua y energía que la proteína animal y produce menos emisiones de gases de efecto invernadero, desechos y contaminación. La proteína vegana también puede ayudar a prevenir la deforestación, la erosión del suelo, la pérdida de biodiversidad y la escasez de agua. La proteína vegana también puede ayudar a reducir el sufrimiento, la explotación y el sacrificio de los animales.
Conclusión
La proteína vegana es más saludable que la proteína animal por muchas razones. La proteína vegana puede reducir el riesgo de enfermedades crónicas, mejorar la digestión y la salud intestinal, favorecer la salud de huesos y músculos y beneficiar el medio ambiente y el bienestar animal. La proteína vegana también puede proporcionar todos los aminoácidos y nutrientes esenciales que el cuerpo humano necesita. Por lo tanto, elegir proteína vegana en lugar de proteína animal puede ser una decisión inteligente y compasiva para tu salud y la del planeta.